Definition
An Access Broker is a cybercriminal or group that specializes in obtaining unauthorized access to computer networks, systems, or databases and then selling that access to other malicious actors, such as ransomware gangs or other threat groups. Access brokers act as intermediaries, providing entry points into target networks that can be exploited for further attacks.
Detailed Explanation
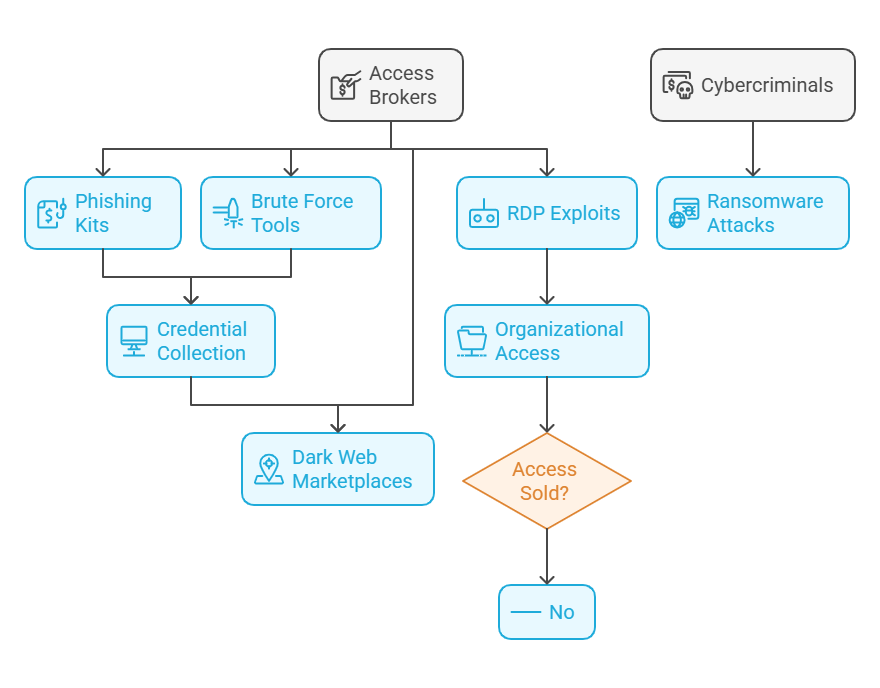
An Access Broker plays a critical role in the cybercrime ecosystem by acquiring and selling credentials or access routes into compromised systems. This access is typically gained through techniques like phishing, credential stuffing, or exploiting software vulnerabilities. Once access is obtained, the broker monetizes it by selling or leasing these entry points on underground forums or dark web marketplaces.
Access brokers allow other cybercriminals to bypass the initial stages of an attack, such as reconnaissance and gaining access, providing a shortcut to more advanced activities like data exfiltration, ransomware deployment, or espionage. The rise of access brokers has contributed to the emergence of Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) and other cybercrime-as-a-service models, making sophisticated attacks accessible to less skilled actors.
For example, an access broker might gain admin access to a corporate network and then sell this access to a ransomware group, enabling them to deploy ransomware within the network and demand a ransom from the organization.
Key Characteristics or Features
- Specialization in Network Access: Focused on finding vulnerabilities in networks and selling entry points rather than directly carrying out attacks.
- Part of Cybercrime Ecosystem: They play a pivotal role in facilitating more complex cyberattacks, like ransomware and data theft.
- Varied Methods for Access: Use techniques such as spear phishing, brute force attacks, or zero-day vulnerabilities to gain access.
- Monetization through Dark Web Marketplaces: Typically operate on dark web forums where they advertise the types of access they have for sale.
Use Cases / Real-World Examples
- Example 1: Corporate Network Access
An access broker may gain unauthorized access to a company’s internal network by exploiting a VPN vulnerability. This access is then sold to a ransomware gang, who use it to deploy ransomware and lock critical company files. - Example 2: Cloud Service Account Access
An access broker might use phishing techniques to obtain credentials for a cloud service account (like AWS or Azure). They then sell these credentials to groups looking to steal data or perform cryptojacking. - Example 3: Database Credentials
An access broker could gain access to a database containing sensitive customer data, then sell that access to a cybercriminal who may extract, sell, or ransom the data.
Importance in Cybersecurity
Access Brokers significantly increase the risk landscape for organizations. Their activities lower the barrier for complex cyberattacks, enabling less sophisticated attackers to carry out high-impact operations. Understanding the role of access brokers can help organizations better prepare against the tactics they use to gain entry, such as phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities in remote access systems.
For cybersecurity professionals, tracking and monitoring access broker activities on dark web forums is crucial for threat intelligence. By identifying potential sales of access to their networks, organizations can take preemptive action to lock down compromised accounts or patch exploited vulnerabilities.
Related Concepts
- Initial Access: The first step in a cyberattack, which access brokers specialize in providing. It refers to gaining an initial foothold in a target network.
- Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS): A service model where access brokers play a role by providing initial access to networks that RaaS operators can exploit.
- Credential Theft: Access brokers often rely on credential theft methods like phishing, brute force, or credential stuffing to gain initial access.
Tools/Techniques
- Phishing Kits: Used by access brokers to collect credentials from targeted users.
- Brute Force Tools: Software tools that automate the process of attempting various password combinations to gain access.
- Dark Web Marketplaces: Platforms where access brokers list compromised access credentials for sale to other criminals.
- Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) Exploits: A common method for access brokers to gain and sell access, especially for targeting organizations using poorly secured RDP services.
Statistics / Data
- A report from Coveware indicates that up to 30% of ransomware attacks in 2023 involved initial access purchased from access brokers.
- According to Digital Shadows, over 500 new access listings are posted monthly on major dark web forums, showcasing the scale of access brokerage in the cybercrime market.
- The price for access varies, with prices ranging from $1,000 to $10,000 depending on the value of the target network and its potential data.
FAQs
How do access brokers differ from ransomware operators?
Access brokers provide the entry point into a system, while ransomware operators use that access to deploy ransomware and demand payment.
What makes access brokers successful?
Their ability to exploit weak security measures, such as unpatched systems, weak passwords, and unsecured remote access protocols.
How can organizations protect themselves against access brokers?
Implementing strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), regular vulnerability patching, and phishing training can help reduce the risk of access brokers gaining entry.
References & Further Reading
- Understanding Access Brokers and Their Role in Ransomware Attacks
- Coveware 2024 Ransomware Report
- Cybersecurity Threats and Mitigations by Bruce Schneier – A guide to understanding how access brokers operate in the modern threat landscape.

0 Comments