Definition
Abuse of Power refers to the misuse or exploitation of authority or control in a system, process, or organization to gain unauthorized benefits, manipulate resources, or circumvent security protocols. In the context of cybersecurity and digital security, it involves using elevated privileges or access rights in ways that violate policy or compromise security.
Detailed Explanation
Abuse of Power occurs when individuals or entities with elevated permissions use their authority to perform actions beyond their intended scope. This might include accessing sensitive information without authorization, tampering with system settings, or bypassing security controls. It is a significant concern in both corporate and governmental environments, where those in positions of power have access to critical data and systems.
In a cybersecurity context, an insider with administrative access may abuse their power by leaking confidential data, disabling security controls, or using their access to conduct espionage or sabotage. Such actions can lead to significant data breaches, compliance violations, and damage to the organization’s reputation. Recognizing and mitigating abuse of power is critical to ensuring robust access control and maintaining trust within a secure environment.
Key Characteristics or Features
- Elevated Privileges Misuse: Often involves misuse of administrator-level access or roles with advanced permissions.
- Violation of Trust: Typically, individuals in trusted positions exploit their role, leading to unauthorized actions.
- Policy Violation: Actions usually contradict the organization’s security policies or ethical guidelines.
- Difficult to Detect: Abuse of power can be challenging to identify as the actions might be performed using legitimate credentials.
Use Cases / Real-World Examples
- Example 1: IT Administrator Access
An IT administrator using their elevated permissions to access and read confidential emails of executives without proper authorization. - Example 2: Insider Threat in Banking
A bank manager using their access to alter customer accounts for personal gain, such as manipulating interest rates or creating false loan approvals. - Example 3: Abuse in Cloud Environments
A cloud service provider employee using their back-end access to manipulate client data or use cloud resources for unauthorized cryptocurrency mining.
Importance in Cybersecurity
Addressing Abuse of Power is crucial for preventing insider threats, which can be more damaging than external attacks due to the access levels involved. Effective management of access controls, implementing the principle of least privilege (PoLP), and continuous monitoring of privileged users are key strategies for preventing such abuses.
For organizations, the risk of abuse of power is particularly relevant during mergers, layoffs, or organizational restructuring, when disgruntled employees might exploit their access. Additionally, compliance frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 emphasize the need for rigorous access control and monitoring to mitigate risks associated with abuse of power.
Related Concepts
- Insider Threat: Abuse of power is a common form of insider threat, where a trusted individual exploits their access to compromise security.
- Privileged Access Management (PAM): A security practice focused on managing and monitoring access by users with elevated privileges to reduce the risk of misuse.
- Least Privilege Principle (PoLP): A strategy to limit access rights for users to the bare minimum required for their role, thus reducing the potential for abuse.
Tools/Techniques
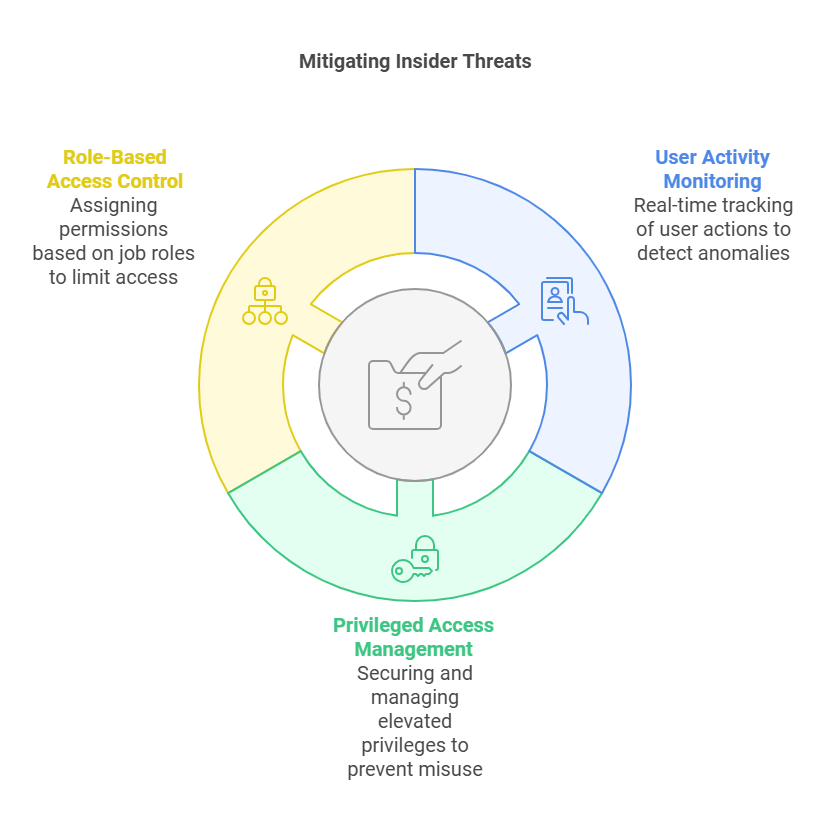
- User Activity Monitoring: Tools like Splunk and SIEM solutions monitor user activities, helping detect potential abuse of power in real-time.
- Privileged Access Management Solutions: Products like CyberArk and BeyondTrust specifically manage and secure accounts with elevated privileges to prevent misuse.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Helps in assigning permissions based on roles, limiting the scope for abuse by restricting access according to job function.
Statistics / Data
- Insider Threat Report 2023 by Ponemon Institute found that 60% of security incidents in organizations involve misuse of privileges by insiders.
- According to a Gartner Study, implementing Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions can reduce the risk of Abuse of Power by up to 50%.
- A survey by Verizon’s Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) indicates that 34% of data breaches involve internal actors, many of which include cases of abuse of power.
FAQs
How does abuse of power relate to cybersecurity?
It involves the misuse of elevated privileges or access by individuals within an organization to perform unauthorized actions that compromise data or security.
What are common signs of abuse of power?
Unusual access patterns, data downloads beyond typical requirements, and changes in system configurations without proper change requests.
How can organizations prevent abuse of power?
By implementing strict access controls, monitoring user activities, conducting regular audits, and using tools like Privileged Access Management (PAM).
References & Further Reading
- Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR)
- Best Practices for Privileged Access Management
- The Insider Threat: A Guide to Understanding, Detecting, and Mitigating by Nick Catrantzos – A detailed guide on preventing insider threats, including abuse of power.

0 Comments